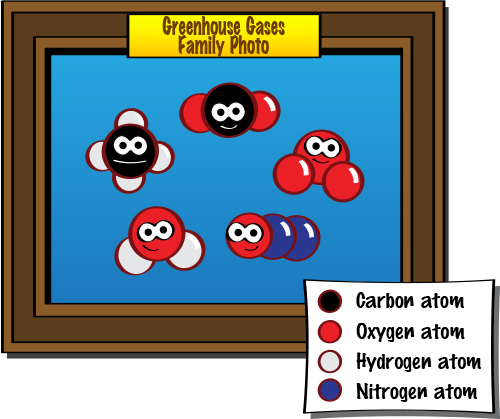
Greenhouse gasses(list top three) 236769
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) makes up the vast majority of greenhouse gas emissions from the sector, but smaller amounts of methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) are also emitted These gases are released during the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, to produce electricityOn 14 July 21, the European Commission adopted a series of legislative proposals setting out how it intends to achieve climate neutrality in the EU by 50, including the intermediate target of an at least 55% net reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 30The package proposes to revise several pieces of EU climate legislation, including the EU ETS, Effort Sharing Regulation, Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as light

Module 12 Mitigation And Adaptation
Greenhouse gasses(list top three)
Greenhouse gasses(list top three)-Absorbed from the airScientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respond
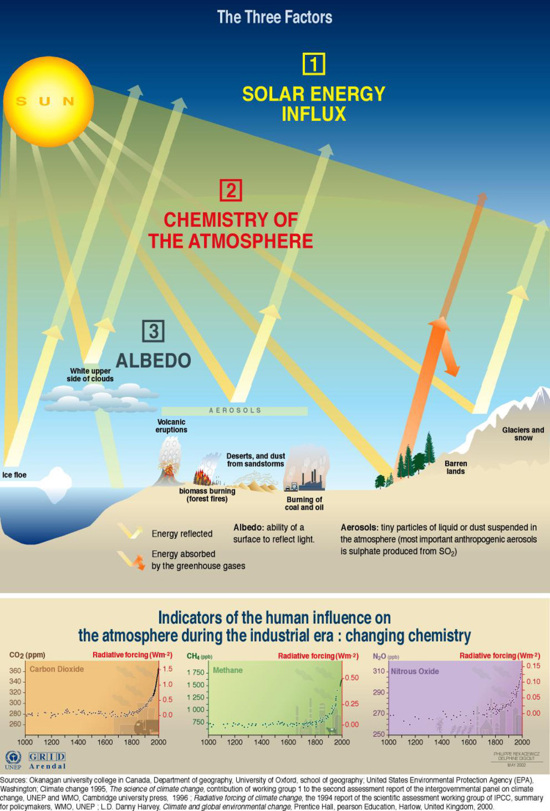



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal
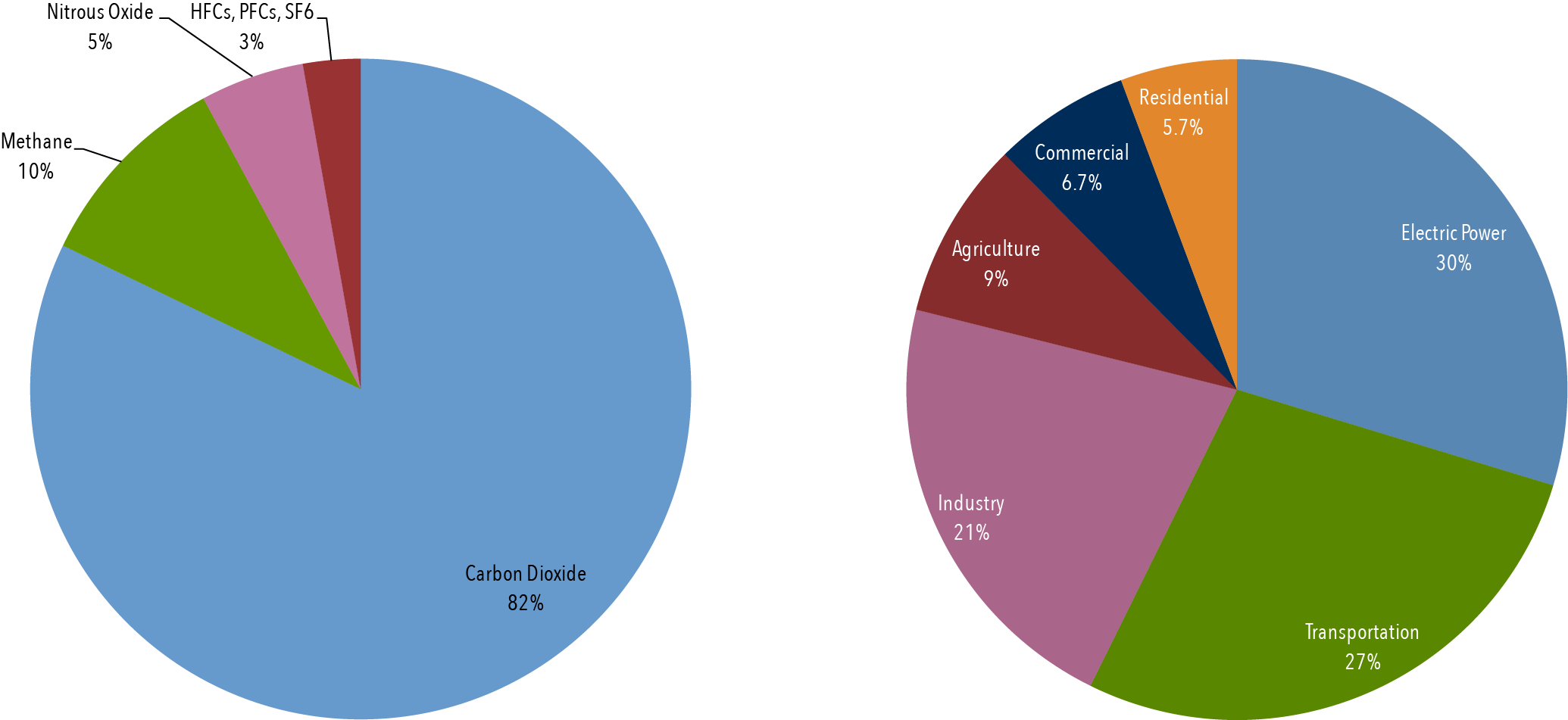
Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphere Australia's 10 highest emitters (scope 1) and proportion of scope 1 emissions from 10 highest emitters The National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (NGER) scheme is a single national framework for corporations to report greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption and energy production The second largest greenhouse gas contributor is the transportation sector which accounts for 26% of all emissions Transportation includes planes, trains, automobiles, buses, trucks, and ships The biggest problem with transportation is its reliance on fossil fuels which produce mainly carbon dioxide More than half of the transportation
By Adhityani Arga 4 Min Read JAKARTA (Reuters) Indonesia is among the world's top three greenhouse gas emitters because of deforestation, peatland degradation and forest fires, a report sponsored The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor Carbon dioxide Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegas emissions The key source of CO2 is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and
Even though greenhouse gases don't make a hard surface like the glass of a greenhouse, but because they have a similar effect in keeping our planet warm, the term "Greenhouse Effect" is a good description The greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbonCement production 278,000 390,000 Methane Fossil fuel production;You are About to View Greenhouse Gas Quantities from Suppliers Important Information about this Data Set Suppliers are facilities or entities that supply certains products (eg, fossil fuels or industrial gases) into the economy that, when combusted, released, or




Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
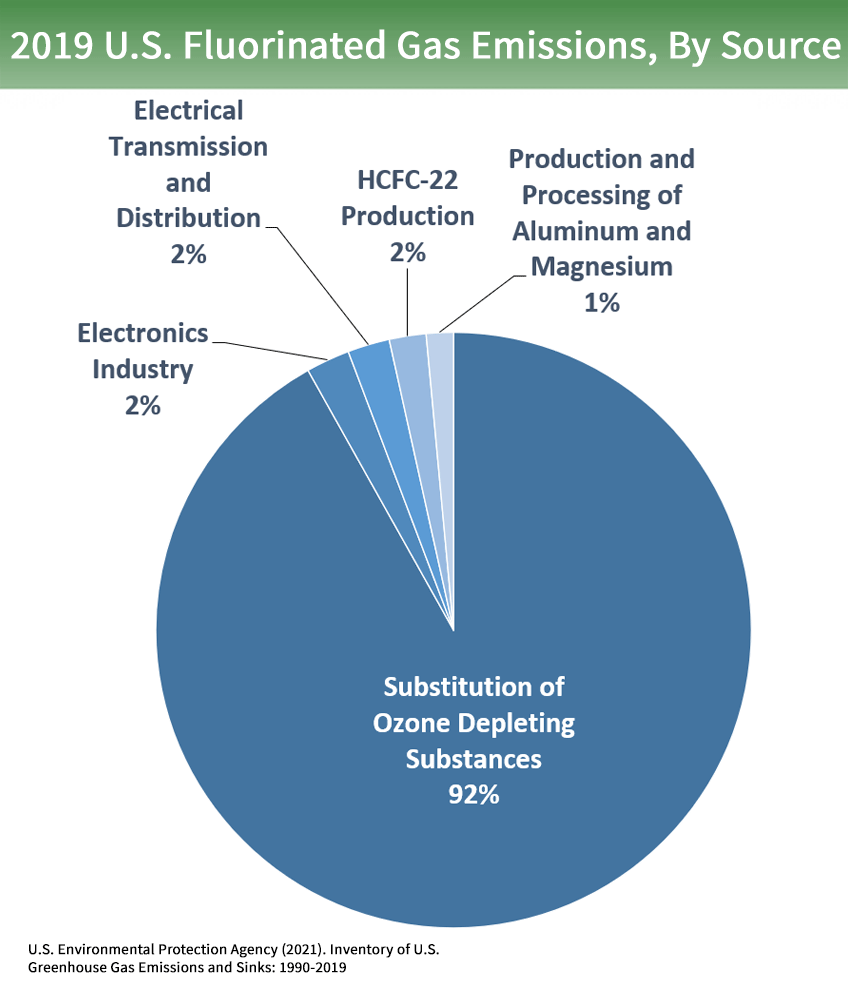
Fluorinated gases Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of industrial processesGreenhouse Gas Emissions from Road Transport Analytical Methods « ISBN 81 77 02 01 1 P Strategies to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Road Transport Analytical Methods Road transport accounts for approximately 80% of CO 2 emissions emanating from transport, which corresponds to more than % of total emissionsAs we discussed in the previous sections, total greenhouse gas emissions are the sum of emissions of various gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and smaller trace gases such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6 ) How much does each gas contribute to global greenhouse gas emissions?




What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society
Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Nitrous Oxide, Methane Share of Global GHG Emissions 103% Virgin Amazon rainforest borders an area of jungle destroyed to make way for farms in Brazil Deforestation, forest degradation and decay, forest and peat fires and other land use changes are responsible for over 10 percent of global emissionsThey are responsible for increasing the temperature of the atmosphere Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), Ozone (O 3 ), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), along with water vapour are known as greenhouse gasesGreenhouse Gas Emissions by Sector and by Gas" pie charts, list the major greenhouse gases and discuss where each of them comes from and which ones are emitted in the largest quantities as a result of people's activities (Note that other lesson plans focus on CO 2 and the greenhouse effect, but you might still want to briefly discuss
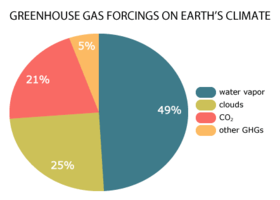



Which Are The Most Common Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Socratic




Climate Change Comic Strip Storyboard By 93bf8b2b
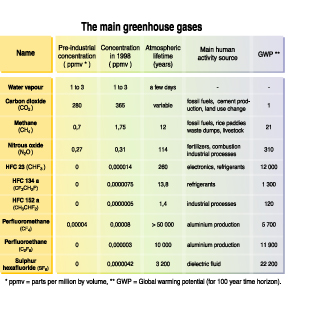
Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such The greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2OGreenhouse gas Major sources Preindustrial concentration (ppb) 11 concentration (ppb) Sources and Concentrations of Major Greenhouse Gases;




Eia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview




Solved 1 List Three Greenhouse Gases 2 Which Is The Most Chegg Com
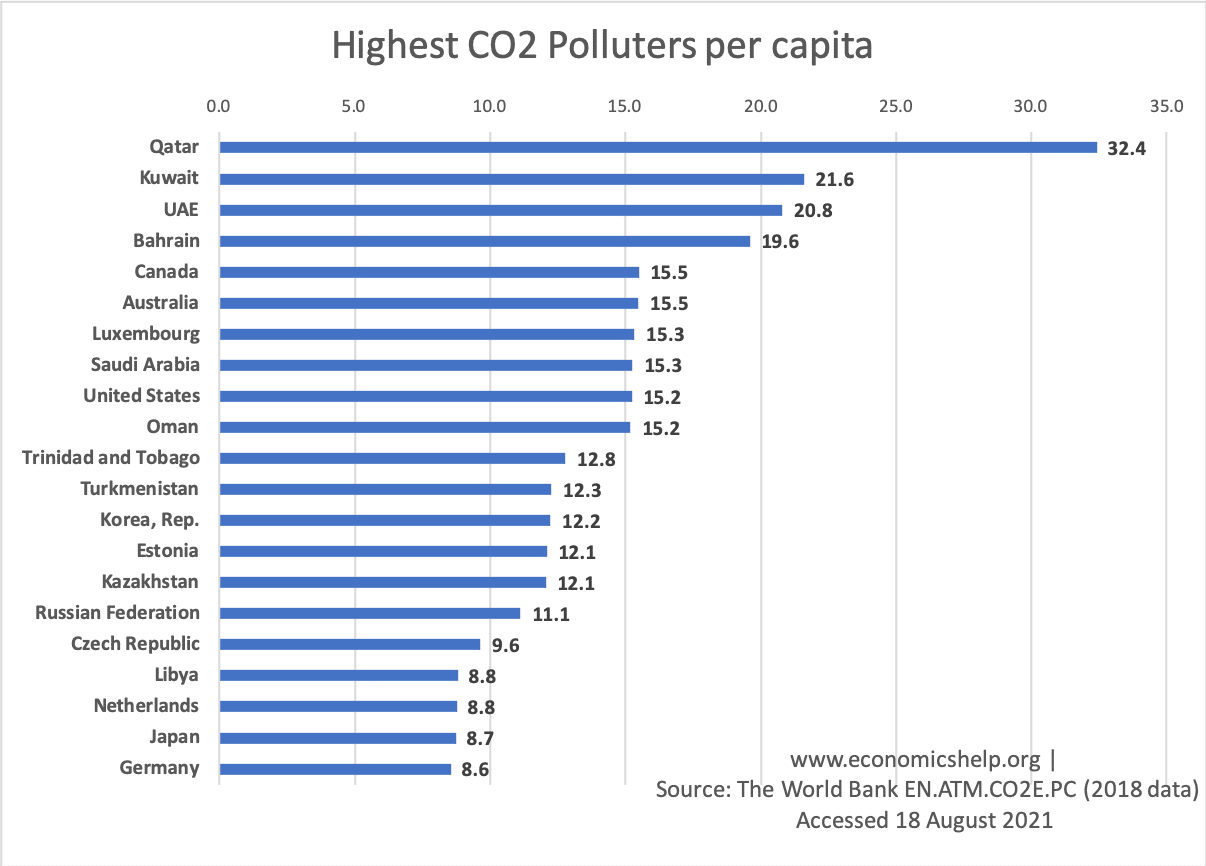
Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Methane (CH 4) Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) References and Resources Water Vapor Greenhouse gases are certain molecules in the air that have the ability to trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere Some greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methane (CH 4 ), occur naturally and play an important role in Earth's climate If they didn't exist, the planet would be a much colder place However, some human activities, such In which case, it would be the world's largest economies China, the United States and Europe That is not entirely fair, though China argues that for each person, the country emits far fewer greenhouse gases If we take a per capita measure, then those countries that produce fossil fuels, and export them, come top of the table




Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Permafrost Pbl
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, The top companies on the list have contributed to 35% of all energyrelated carbon dioxide and methane worldwide, totalling 480bn tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (GtCO 2 e) since 1965 Q&A Greenhouse gases trap heat and make the planet warmer Human activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over the last 150 years 1 The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities in the United States is from burning fossil fuels for electricity, heat, and transportation




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Warmup What Are Three Natural Ways In Which Climate Changes What Timescale Do These Processes Generally Occur Ppt Download
It is based on data for carbon dioxide, methane ( CH 4 ), nitrous oxide ( N 2O ), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) emissions compiled by the World Resources Institute (WRI)Carbon Dioxide Fossil fuel combustion;Click for a text description of Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas 10 Carbon dioxide/CO 2 fossilfuel use 65% Carbon dioxide/CO 2 (deforestation, decay of biomass, etc) 11%
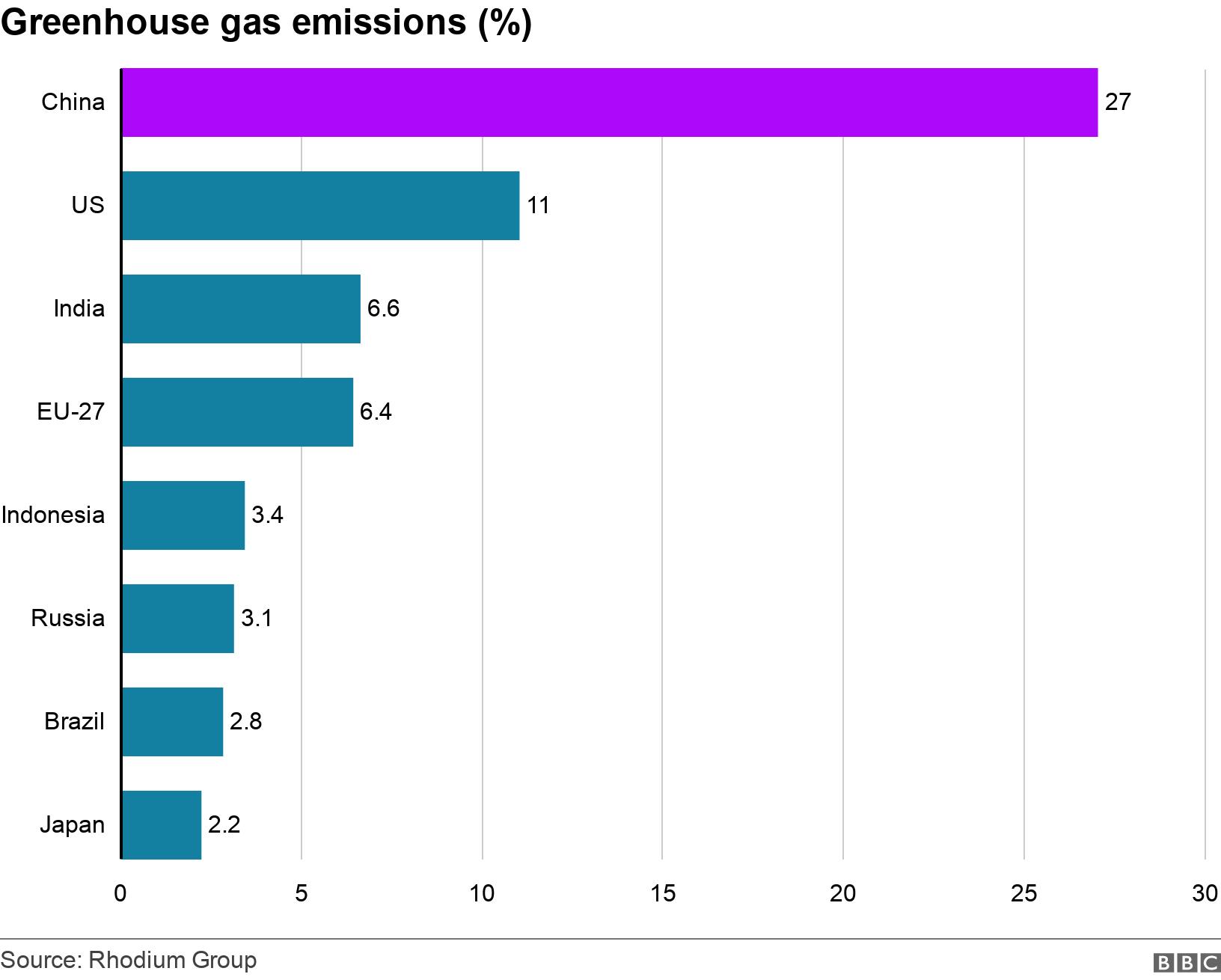



Report China Emissions Exceed All Developed Nations Combined c News




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja
greenhouse effect warming when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere The greenhouse effect is the retention by Earth's atmosphere in the form of heat some of the energy that arrives from the sun as light CO2 a heavy odorless colorless gas formed during respiration and by the decomposition of organic substances;Of CH 4 absorbs radiative energy 25 times more effectively than each molecule of CO 2, and CFC12 is 15,800 times more effective than CO 2 on a per molecule basis and, since molecules of the two gases have different mass, 5,750 times more effective on a per mass basis Figure 32 incorporates a simple extrapolation of current atmospheric transformation ratesTo stop climate change, we need to stop the amount of greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, from increasing For the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests, which naturally pull carbon dioxide out of the air, has caused greenhouse gas levels to increase There are two main ways to stop the amount of greenhouse gases from increasing we can stop




Greenhouse Gases Have Soared To Record Levels Wmo Climate Central




5 Charts Show How Your Household Drives Up Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pbs Newshour Weekend
Most of the world's greenhouse gas emissions come from a relatively small number of countries China, the United States, and the nations that make up the European Union are the three largest emitters on an absolute basis Per capita greenhouse gas emissions are highest in the United States and Russia Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions, 1850 US greenhouse gas emissions fell 103% in , the largest drop in emissions in the postWorld War II era, as the coronavirus crippled the economy, according to a report released Tuesday by theGreenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3)
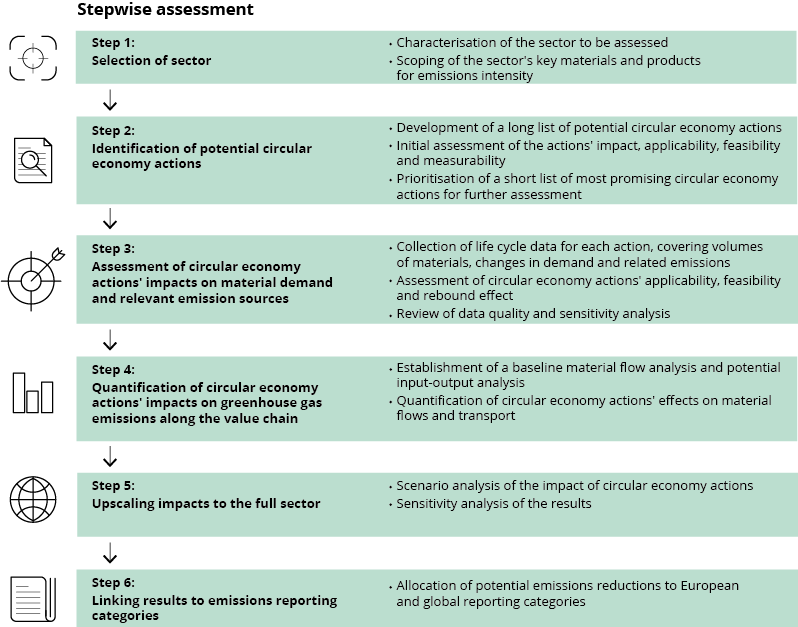



Cutting Greenhouse Gas Emissions Through Circular Economy Actions In The Buildings Sector European Environment Agency



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data
Landfills 722 1,803 Nitrous OxideSince the Industrial Revolution, rising emissions of greenhouse gases —including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and others—have been the driving force behind climate change Who is




Climate Change Lesson Plan




Aluminium Sector Greenhouse Gas Pathways To 50 International Aluminium Institute




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Solved Topics To Be Answered 1 Explain What Is Meant By Chegg Com
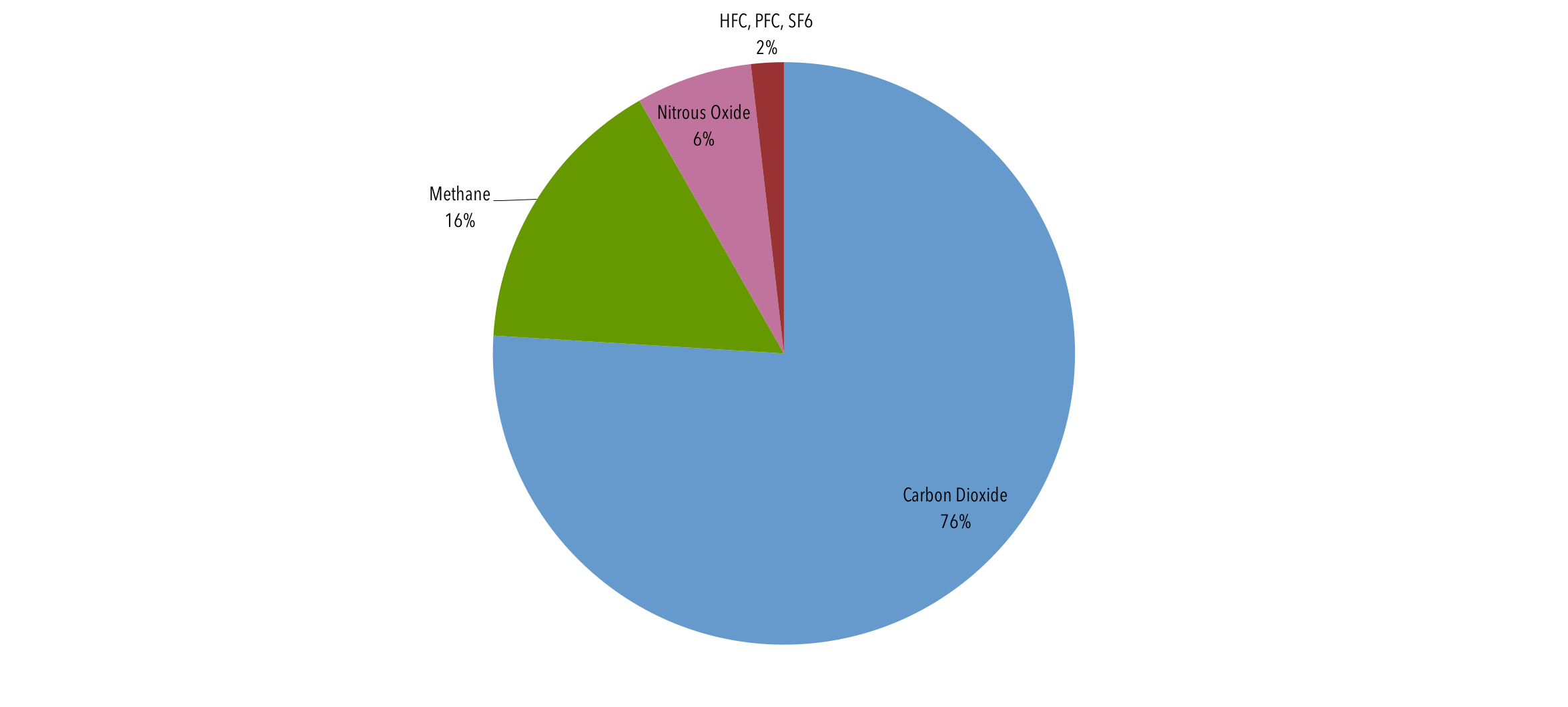



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus




The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions In One Graphic Climate Central



Main Sources Of Carbon Dioxide Emissions What S Your Impact
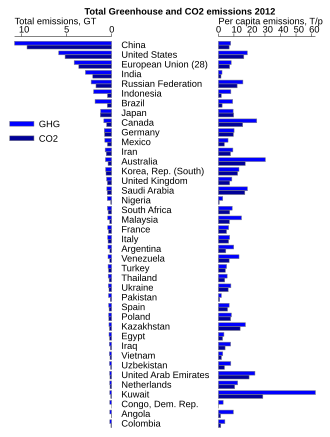



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Embodied Ghg Emissions Of Buildings The Hidden Challenge For Effective Climate Change Mitigation Sciencedirect



1




List Three Greenhouse Gases 2 Which Is The Most Important Of These Gases In Terms Of Amplification Of Climate Effects 3 Describe How These Gases Course Hero




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament




Revealed The Firms Behind A Third Of All Carbon Emissions Climate Crisis The Guardian
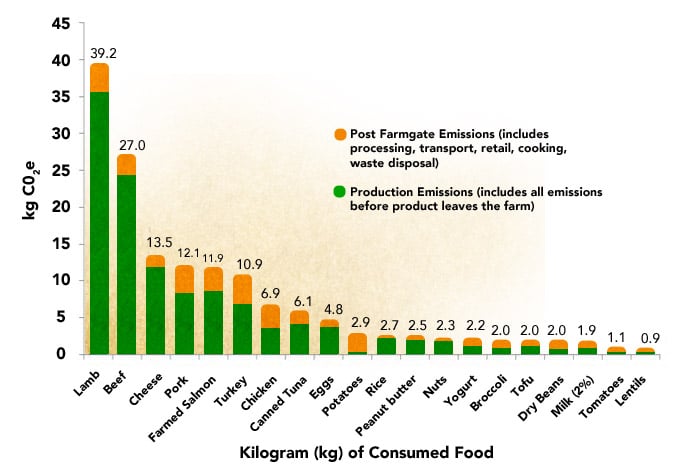



The Impacts 11 Meat Eaters Guide Meat Eater S Guide To Climate Change Health Environmental Working Group




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Solved Question 8 0 1 Pts List Three Major Sources Of Chegg Com
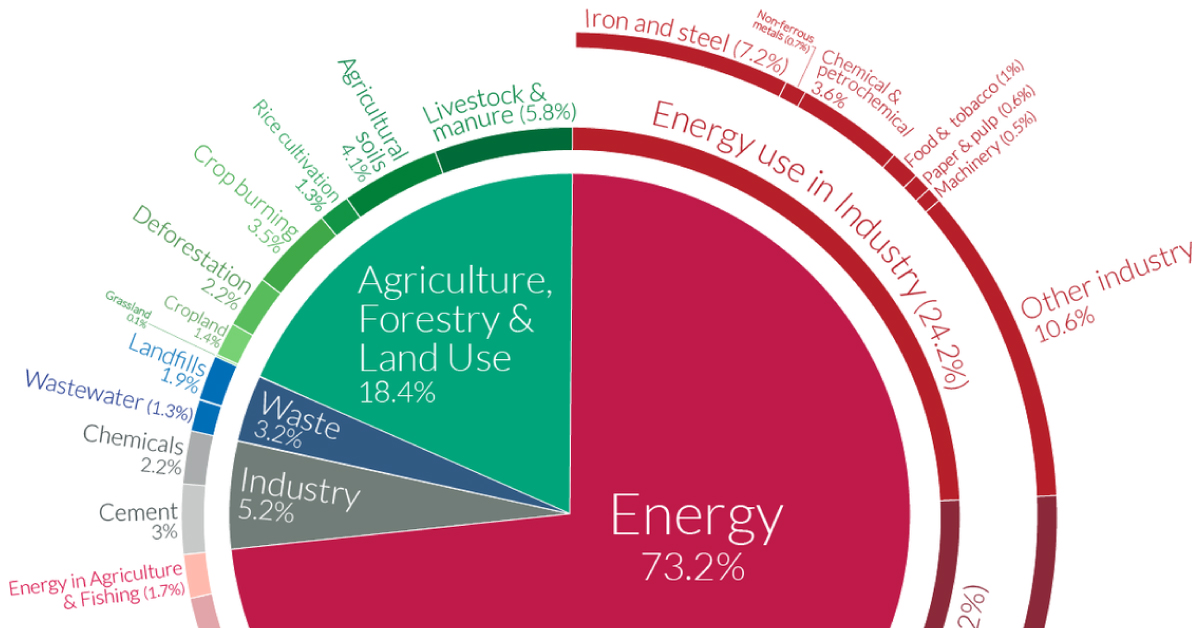



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




The Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gasses




The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Carbon Dioxide




Solved 1 Please Define The Greenhouse Gas And List Three Of Them And The Major Source Of One Of The Greenhouse Gases Explain The Climate Change And Greenhouse Effect 2 2 Please Identify




Module 12 Mitigation And Adaptation




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Growth Of 1 1 In Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 19 Pbl Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
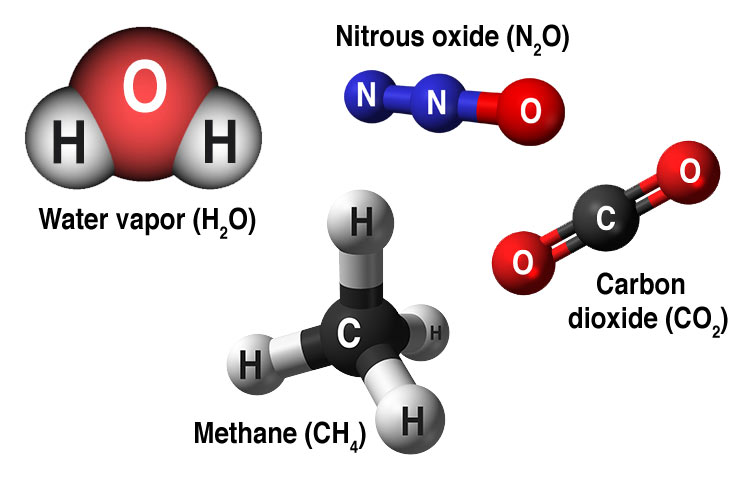



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Carbon Intensive Industries The Industry Sectors That Emit The Most Carbon Eco Warrior Princess




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Solved Name Chem 122 Volcanoes And Acid Rain 1 Which Of Chegg Com
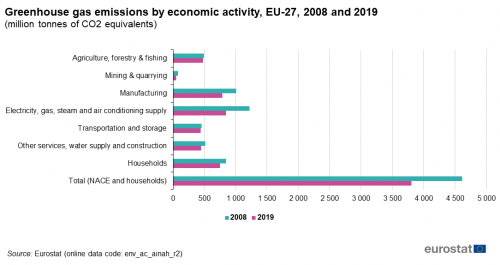



Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Air Emissions Accounts Statistics Explained
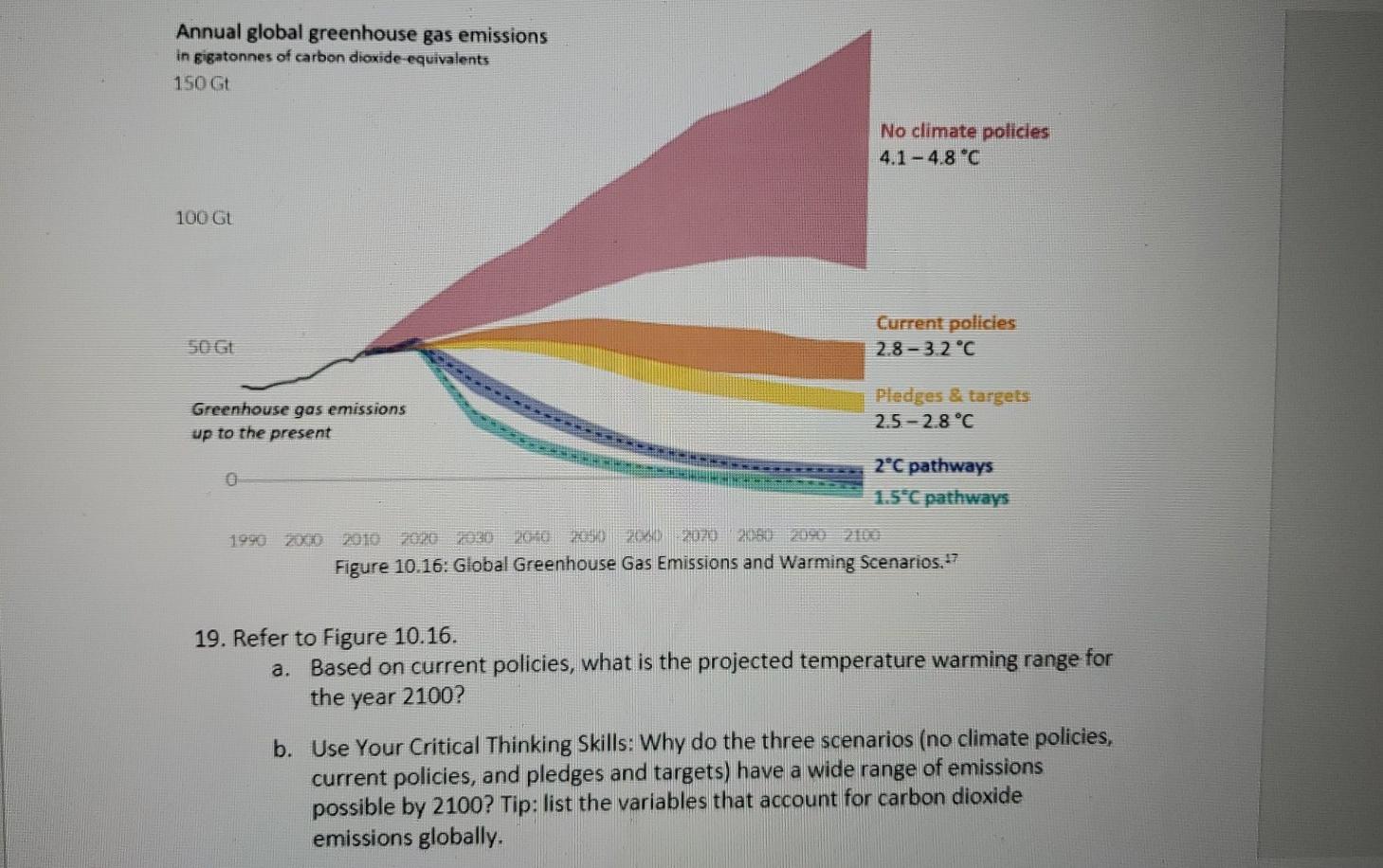



Solved Annual Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Gigatonnes Chegg Com



1




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica
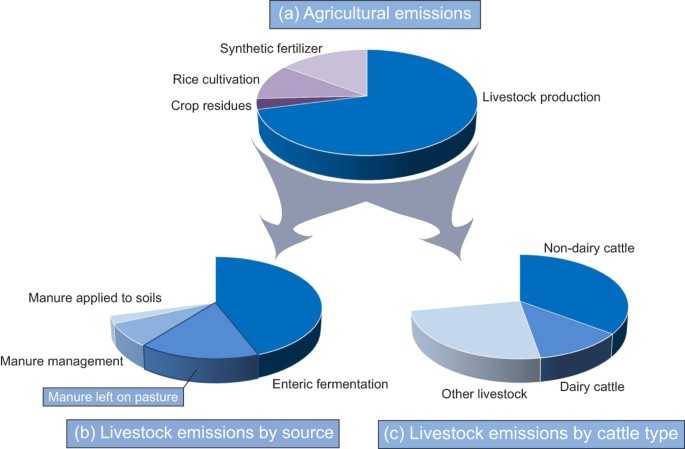



The Role Of Dung Beetles In Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Cattle Farming Scientific Reports




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




What Are The Main Man Made Greenhouse Gases Environment The Guardian




Pdf Erratum To Household Preferences For Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Four European High Income Countries Does Health Information Matter A Mixed Methods Study Protocol




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Ipcc List Of Greenhouse Gases Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Most Important Greenhouse Gases Are Absorbers Of Long Wave Radiations From Earth Transparent To Both Solar Radiations And Long Wave Radiations From Earth Absorbers Of Solar Radiations For Warming The Atmosphere Transparent To Emissions
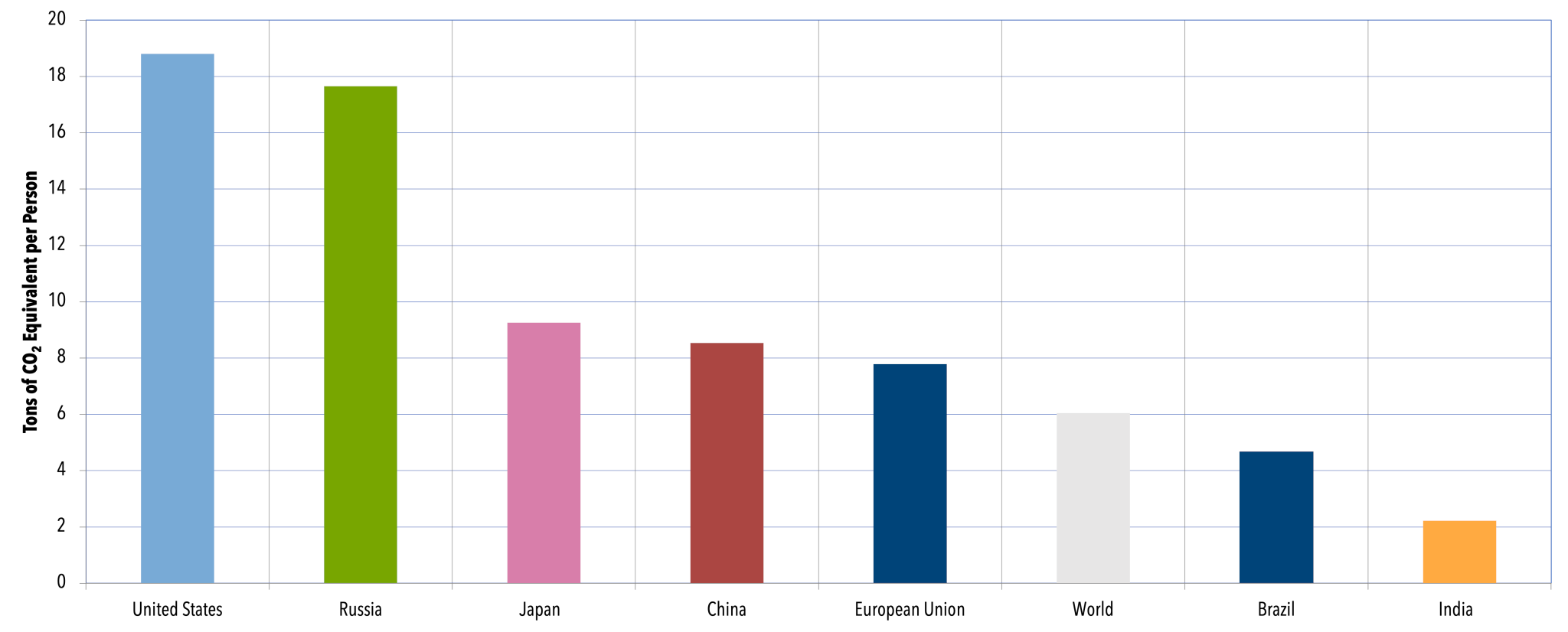



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Top Co2 Polluters And Highest Per Capita Economics Help



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming



Total Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends And Projections In Europe European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
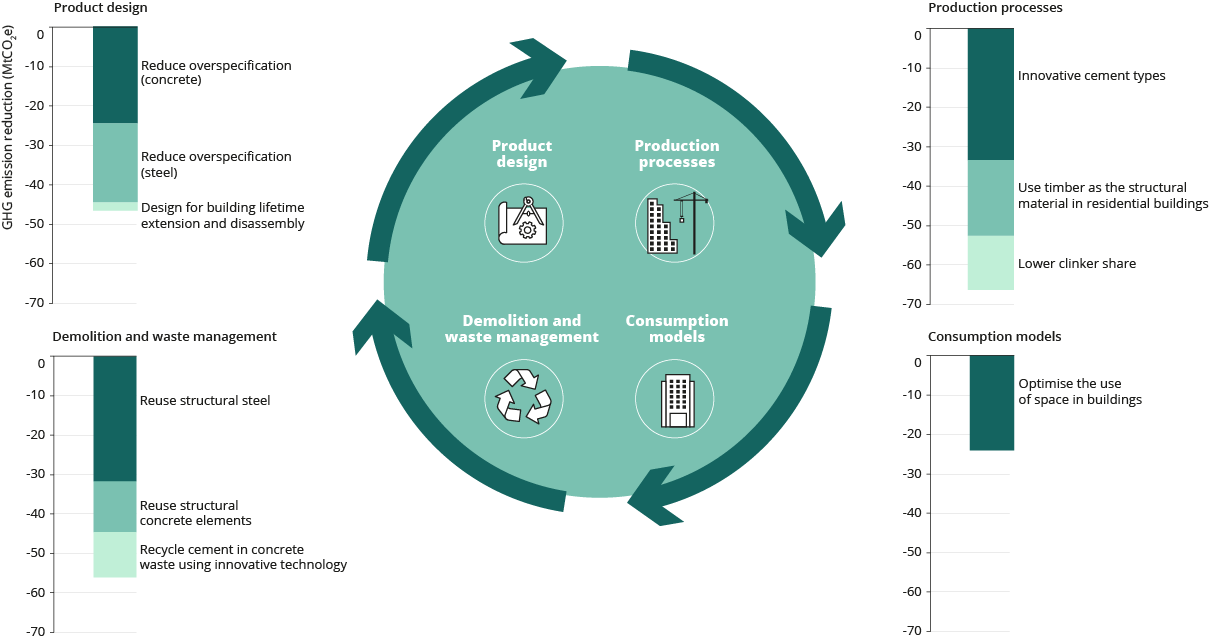



Cutting Greenhouse Gas Emissions Through Circular Economy Actions In The Buildings Sector European Environment Agency




Eia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
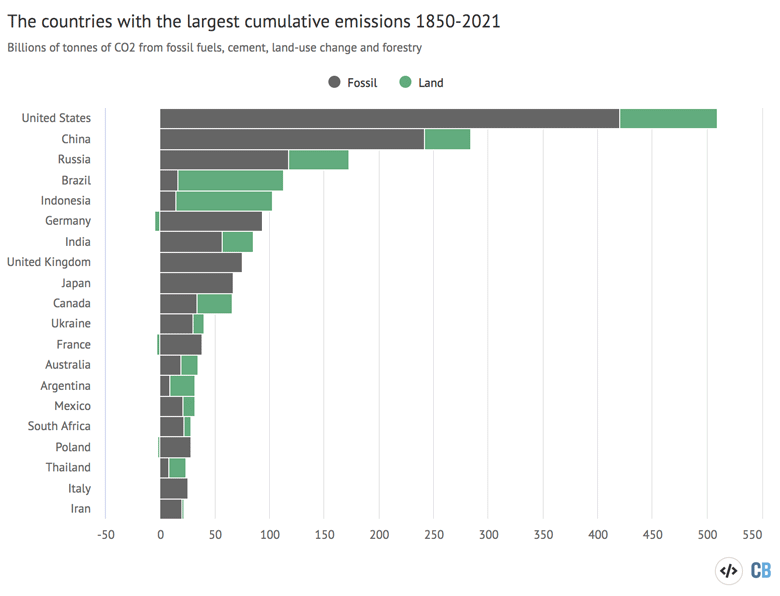



Analysis Which Countries Are Historically Responsible For Climate Change Carbon Brief




List Of Countries By Greenhouse Gas Emissions Per Person Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
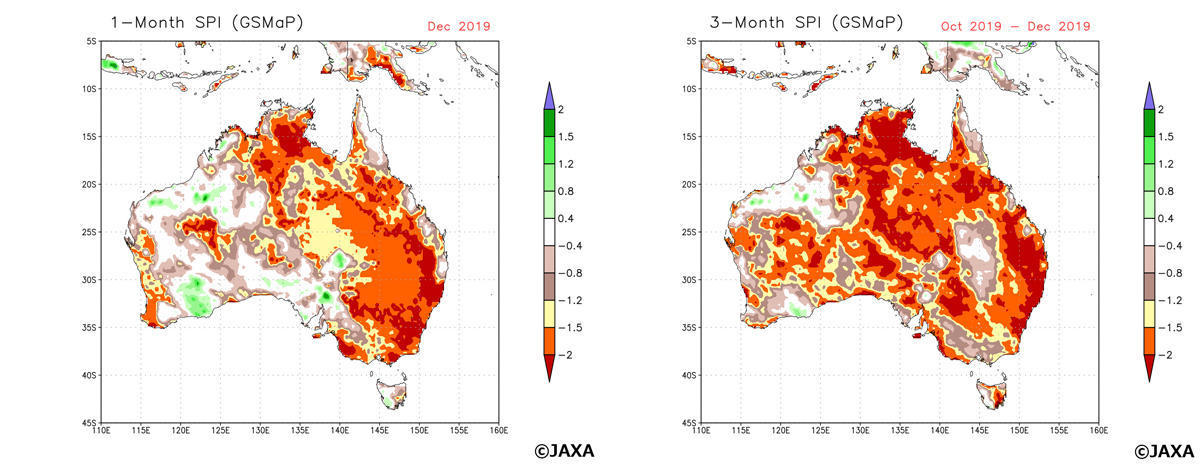



Jaxa Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite Ibuki Gosat



Energy Agriculture Industry Waste The Main Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Georgia Georgia Today On The Web




Uk Tops List Of World S Biggest Greenhouse Gas Emitters Carbon Brief
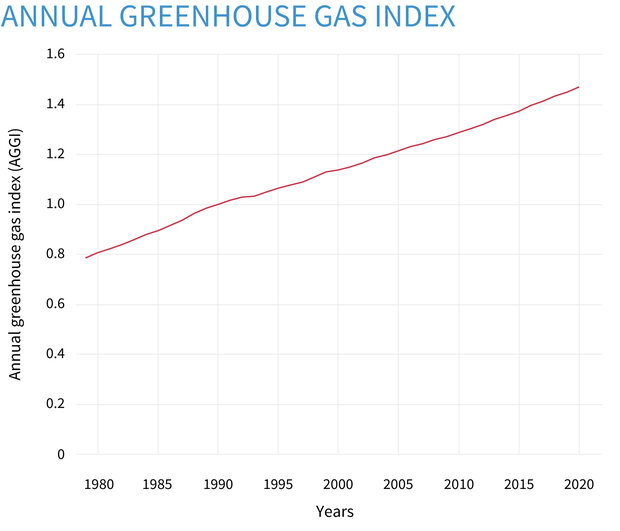



Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Reducing Greenhouse Gases Washington State Department Of Ecology




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Climate Change And Impacts Accelerate World Meteorological Organization




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know




China Us These Countries Produce The Most Co2 Emissions




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



Solved Question 18 3 Points List Three Major Blogenic Chegg Com



1



Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
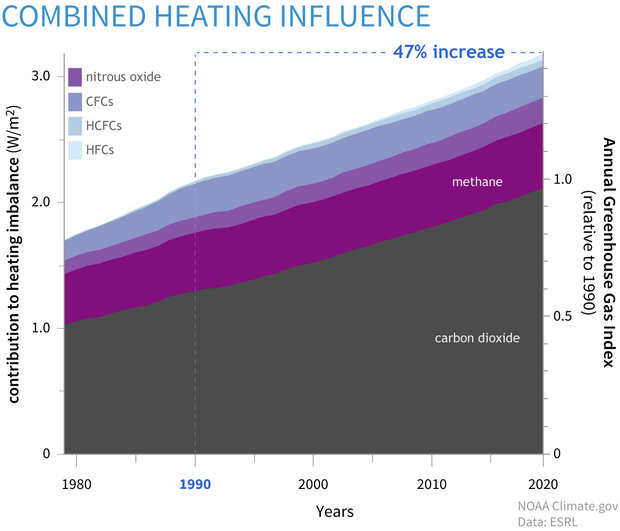



Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica



The Main Greenhouse Gases Grid Arendal
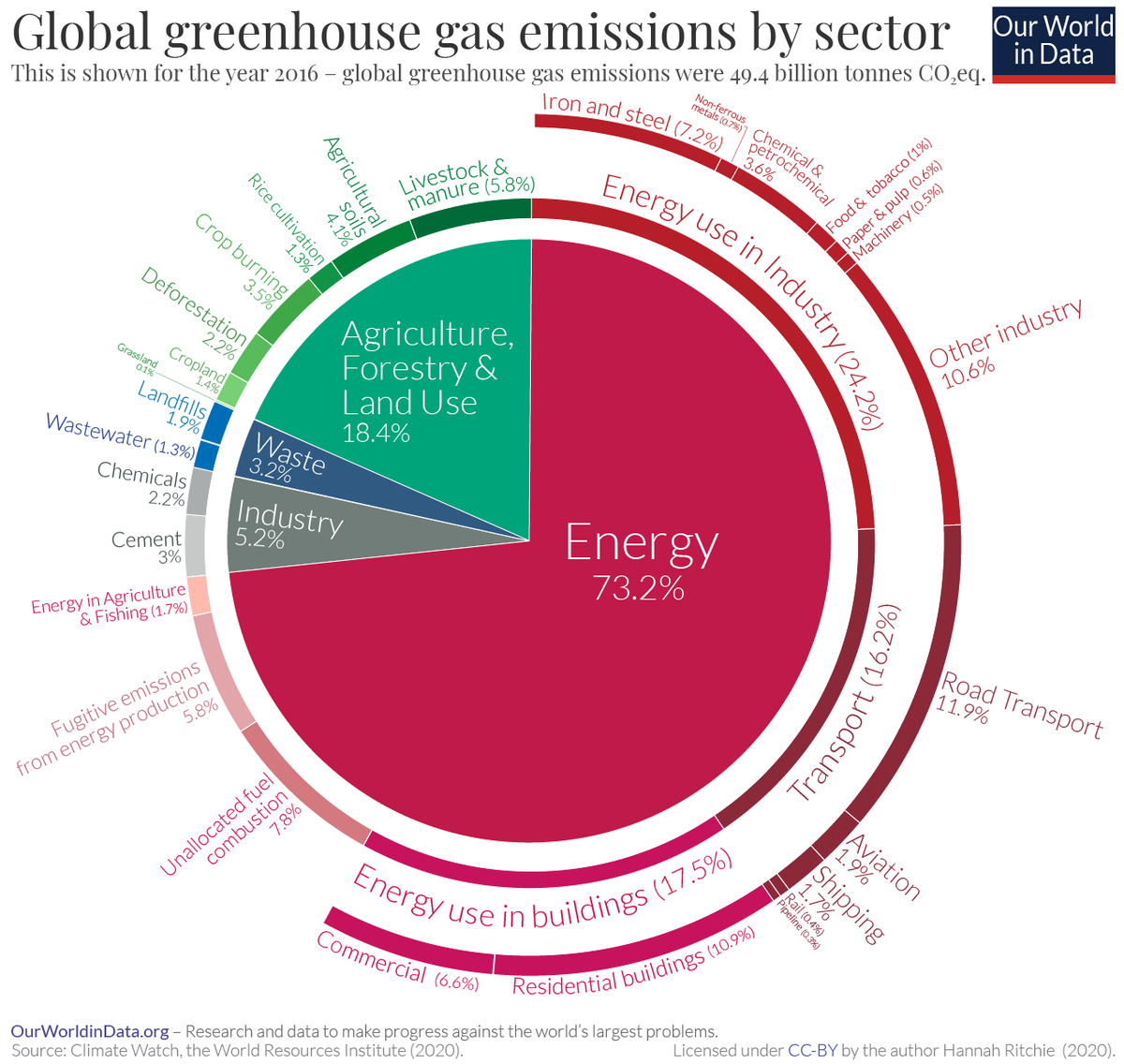



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector
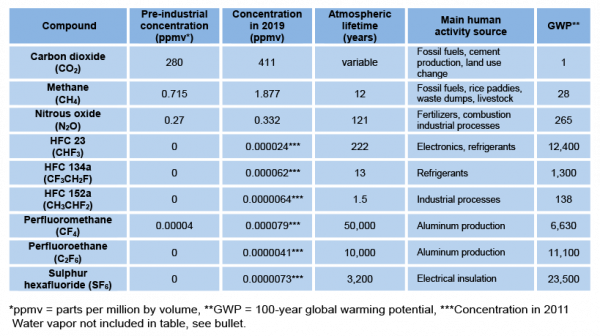



Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems



Top 3 Co2 Emitters For 19 In Bulgaria Croatia Greece Cyprus Romania Slovenia




Just 100 Companies Responsible For 71 Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Report Says The Independent The Independent




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In 18 Source Epa 15 Overview Of Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus
コメント
コメントを投稿